References
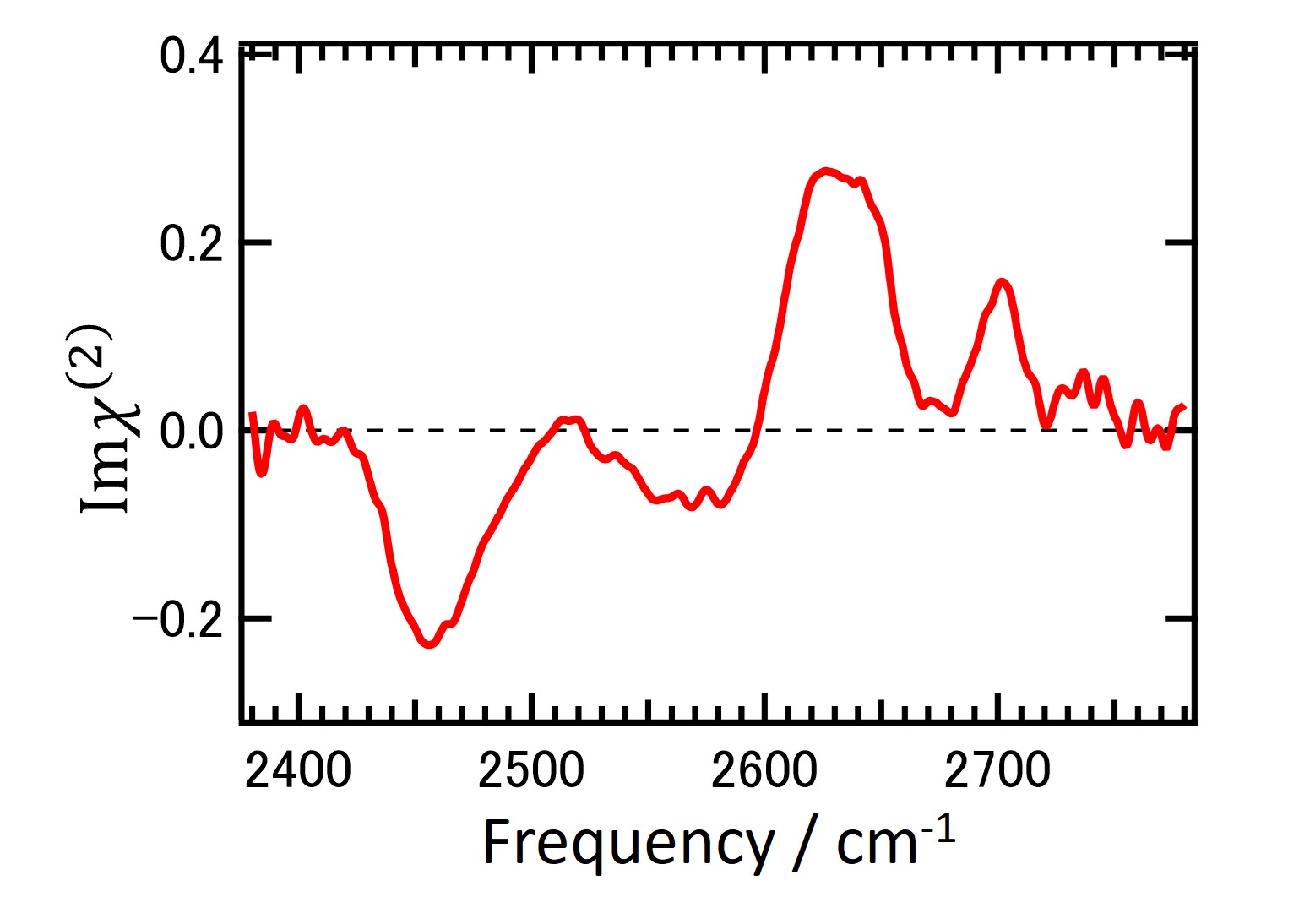
1. "Proton Configuration in Water Chain on Pt(533)" Naoki Nagatsuka, Noboru Shibata, Toya Muratani, and Kazuya Watanabe, JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY LETTERS, 2022, 8, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c01378 .
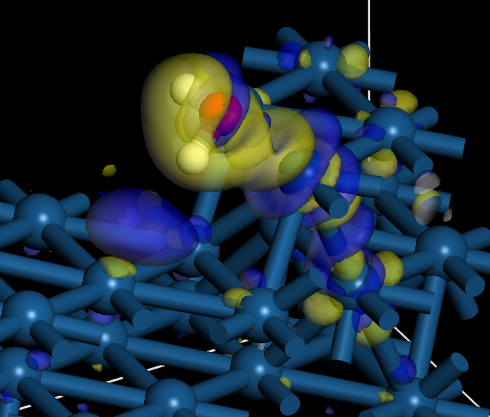
2. "Hydroxyl Formation on Pt(553)" N. Nagatsuka, S. Kamibashira, N. Shibata, T. Koitaya, K. Watanabe, J. Phys. Chem. C, 127, 8104-8112 (2023).
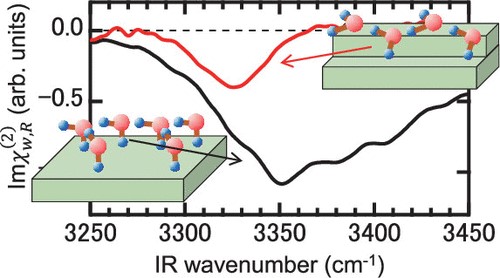
3."Water orientation on platinum surfaces controlled by step sites" Naoki Nagatsuka, Takumi Otsuki, Shota Kamibashira, Takanori Koitaya, Kazuya Watanabe, J. Chem. Phys. 161, 094705 (2024). (Selected as Editor's Pick)